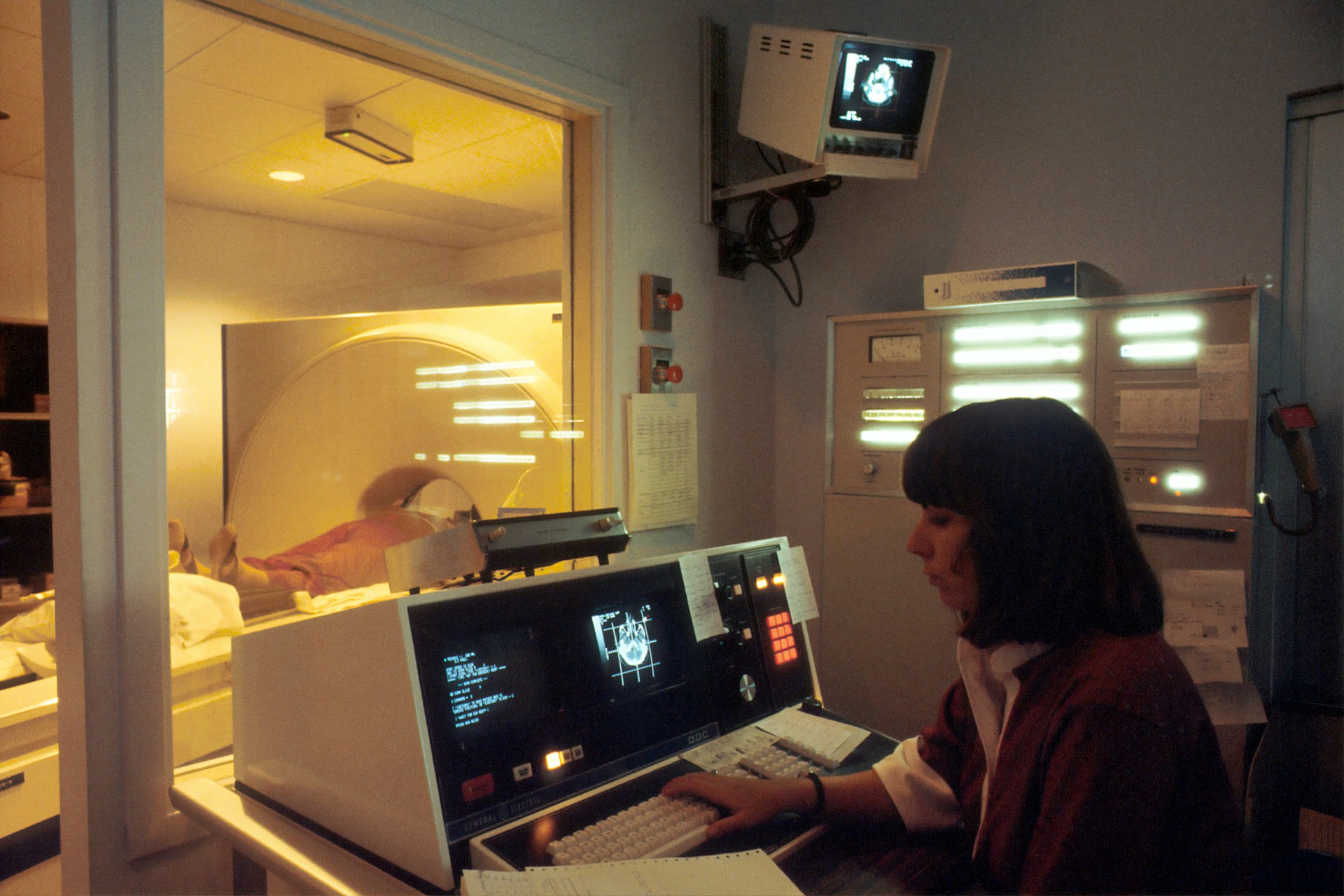
In recent years, the focus on radiation protection in medical imaging has intensified. As healthcare professionals, UK radiographers play a crucial role in minimizing radiation exposure during imaging procedures. The mission is to ensure diagnostic accuracy while safeguarding patients from unnecessary radiation. This article delves into the latest techniques and technologies that UK radiographers are utilizing to reduce radiation doses, providing a comprehensive overview of the advancements in this field.
The Importance of Dose Reduction in Medical Imaging
Radiation exposure is a necessary aspect of many medical imaging procedures, including computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine. However, the potential risks associated with ionizing radiation cannot be overlooked. Exposure to high levels of radiation can lead to harmful effects, making it essential to employ strategies that minimize the effective dose received by the patient.
This might interest you : How can UK community pharmacists improve medication management for elderly patients with complex conditions?
UK radiographers are at the forefront of implementing dose reduction techniques. They leverage advancements in technology and adhere to stringent guidelines to keep radiation doses as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA). The emphasis on dose reduction is not only about enhancing radiation protection but also about improving patient care and safety.
A recent study published on PubMed highlights the critical nature of dose management. By constantly updating their practices to include the latest diagnostic reference levels, radiographers ensure that patients receive only the necessary amount of radiation for accurate diagnosis. This section will explore some of the most effective dose reduction techniques currently employed.
In the same genre : What emerging digital health tools can UK health professionals use to support patients with chronic conditions?
Advanced Imaging Technology and Software
The rapid development of medical imaging technology has significantly contributed to reducing radiation doses. Modern imaging systems, equipped with sophisticated software, allow for better image quality with lower radiation requirements.
For instance, CT scanners now feature iterative reconstruction techniques that enhance image clarity while reducing radiation exposure by up to 60%. Similarly, advancements in fluoroscopy and nuclear medicine have led to the development of equipment that requires less radiation to produce high-quality images.
UK radiographers use automated exposure control systems that adjust the radiation dose based on the size and density of the body part being imaged. This tailored approach ensures that the patient receives the minimum dose necessary for a clear diagnostic image. Additionally, dose-tracking software provides real-time feedback, allowing radiographers to monitor and adjust radiation levels during imaging procedures.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging has also shown promise in further reducing radiation exposure. AI algorithms can predict the minimum effective dose for various imaging scenarios, aiding radiographers in making more informed decisions. This synergy between human expertise and technological advancements is pivotal in enhancing patient safety.
Protocol Optimization and Patient-Specific Adjustments
Standardizing imaging protocols and customizing them for individual patients are key strategies for dose reduction. UK radiographers meticulously review and update imaging protocols to ensure they align with the latest diagnostic reference levels and guidelines.
One such approach is the use of child-specific protocols in pediatric imaging. Children are more susceptible to the harmful effects of ionizing radiation, making dose optimization crucial. By adjusting scan parameters, radiographers can significantly reduce radiation exposure in young patients without compromising diagnostic quality.
For adults, weight-based protocol adjustments are employed. Heavier patients require higher doses for adequate image penetration, but overexposure can be avoided by fine-tuning the parameters. This patient-specific approach is supported by continuous training and education, ensuring radiographers are adept at implementing the most effective techniques.
Furthermore, reducing unnecessary imaging through careful patient assessment is an essential practice. UK radiographers collaborate with referring physicians to evaluate the necessity of each imaging procedure, thereby avoiding unnecessary radiation. This judicious use of imaging not only protects patients but also optimizes resource utilization within the healthcare system.
Utilization of Radiation Protection Devices
In addition to technological and procedural advancements, the use of physical radiation protection devices is a fundamental aspect of dose reduction. Lead aprons, thyroid shields, and gonadal shields are standard tools that protect sensitive body parts from ionizing radiation during imaging procedures.
UK radiographers are also incorporating advanced protective materials such as bismuth shielding. Bismuth shields are lightweight and provide effective protection, particularly in CT imaging. These shields can be placed over sensitive areas like the breasts and thyroid without significantly affecting image quality.
Another innovative approach is the use of beam collimation in X-ray and fluoroscopy procedures. By narrowing the X-ray beam to the area of interest, radiographers can minimize radiation exposure to surrounding tissues. This technique not only reduces the effective dose but also enhances image contrast, aiding in more accurate diagnosis.
Moreover, time spent under radiation is a critical factor. Techniques like pulsed fluoroscopy reduce the duration of exposure by emitting radiation in short bursts rather than continuously. This method is particularly beneficial in procedures requiring real-time imaging, such as interventional radiology.
Continuous Education and Research
Ongoing education and research are paramount in advancing radiation protection practices. UK radiographers are encouraged to participate in continuous professional development programs and stay updated with the latest research findings.
Platforms like Google Scholar and PubMed provide access to a wealth of research articles and studies on radiation dose reduction. By staying informed, radiographers can implement evidence-based practices and adapt to emerging technologies and protocols.
Collaborative research projects within the UK and internationally also play a significant role. These projects often focus on developing new techniques and evaluating the effectiveness of existing ones. For instance, recent studies available on PubMed Google have explored the impact of AI and machine learning in dose optimization, providing valuable insights for clinical practice.
Furthermore, patient education is an integral part of the process. By informing patients about the potential risks and benefits of imaging procedures, radiographers can foster a more informed and cooperative patient population. This collaborative approach enhances the overall effectiveness of radiation protection strategies.
In conclusion, the quest to reduce radiation exposure during medical imaging procedures is a multifaceted endeavor, driven by technological advancements, protocol optimization, protective devices, and continuous education. UK radiographers are leading the way in implementing these techniques, ensuring that patients receive the safest and most effective diagnostic care possible.
By employing advanced imaging technology, customizing protocols, utilizing protective devices, and staying abreast of the latest research, radiographers minimize radiation doses while maintaining diagnostic accuracy. The collective effort to reduce unnecessary radiation exposure underscores the commitment to patient safety and quality care.
As the field of medical imaging continues to evolve, the dedication to radiation protection remains unwavering. Through innovation and education, UK radiographers will continue to enhance their practices, ensuring a safer future for all patients undergoing imaging procedures.